Understanding Virtualisation
Understanding Virtualisation
In
computing, virtualisation refers
to the act of creating a virtual (rather than actual) version of something,
including virtual computer
hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources
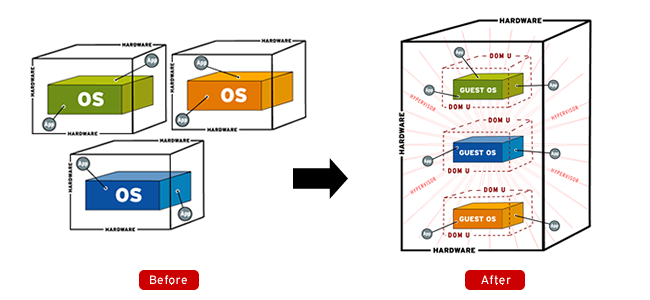
1. OS Virtualisation
Operating system
virtualisation refers to the use of software to allow system hardware to run multiple instances of different operating
systems concurrently,
allowing you to run different applications requiring different operating systems on one computer system. The operating systems do not interfere
with each other or the various applications.
2. Application-Server Virtualisation
Server virtualisation is
the partitioning of a physical server into smaller virtual servers to help maximise
your server resources. In server virtualisation the resources of the
server itself are hidden, or masked, from users, and software is used to divide
the physical
server into multiple
virtual environments, called virtual or private servers. This is in contrast
to dedicating one server to a
single application or task.
3. Application Virtualisation
Application
virtualisation is
software technology that encapsulates computer
programs from
the underlying operating system on
which it is executed. A fully virtualised application is not
installed in the traditional sense, although it is still
executed as if it were. The application behaves at run time like it is directly interfacing
with the original operating system and all the resources managed by it, but can
be isolated or sandboxed to
varying degrees.
4. Network
Network virtualisation is a method of combining the
available resources in a network by splitting up the
available bandwidth into channels, each of which is independent
from the others, and each of which can be assigned (or reassigned) to a
particular server or device in real time. Each channel is independently
secured. Every subscriber has shared access to all the resources on the network
from a single computer.
5. Storage Virtualisation
Storage
virtualisation is the amalgamation of multiple network storage devices into
what appears to be a single storage unit. Storage virtualisation is usually
implemented via software applications and often used in SAN (storage area network), a high-speed sub
network of shared storage devices, and makes tasks such as archiving, back-up, and recovery easier and faster.
Benefits of Virtualisation
·
Increased security.
·
Longer hardware refresh cycles.
·
Allows moves to the cloud.
·
Efficient IT infrastructure.
·
More efficient software installations and
hardware deployment.
·
Less energy consumption and maintenance cost.
·
Immediate access to files and applications.
·
Quick and easiest way of backup and disaster
recovery.
·
Less operating costs.
·
Ability to use thin clients (thin client is a
lightweight computer that is purpose built for remote access to a server. All
computations are done on the remote server).
·
Less time spent on providing support to desk
side.
#AcmaComputers, #AnnualMaintenanceContract, #PcRepairServices, #DesktopSupportServices, #LaptopSupportServices, #ComputerSupportServices, #Firewall, #DataBackup, #CCTV & IP Cameras, #Servers, #Computer viruses, #softwares, #IT Security , #Virtualisation


Comments
Post a Comment